Introduction
Stakeholder Management is an important discipline that successful architecture practitioners can use to win support
from others. It helps them ensure that their projects succeed where others fail.
The benefits of successful Stakeholder Management are that:
-
The most powerful stakeholders can be identified early and their input can then be used to shape the architecture;
this ensures their support and improves the quality of the models produced.
-
Support from the more powerful stakeholders will help the engagement win more resource, thus making the
architecture engagement more likely to succeed.
-
By communicating with stakeholders early and frequently, the architecture team can ensure that they fully
understand the architecture process, and the benefits of enterprise architecture; this means they can support the
architecture team more actively when necessary.
-
The architecture engagement team can more effectively anticipate likely reactions to the architecture models and
reports, and can build into the plan the actions that will be needed to capitalize on positive reaction whilst
avoiding or addressing any negative reactions.
It is essential in any initiative to identify the individuals and groups within the organization who will contribute to
the development of the architecture, identify those that will gain and those that will lose from its introduction, and
then develop a strategy for dealing with them.
Approach to Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder analysis should be used during Phase A (Architecture Vision) to identify the key players in the engagement,
and also be updated throughout each phase; different stakeholders may be uncovered as the engagement progresses through
into Opportunities & Solutions, Migration Planning, and Architecture Change Management.
Complex architectures are extremely hard to manage, not only in terms of the architecture development process itself,
but also in terms of obtaining agreement from the large numbers of stakeholders touched by it.
For example, just as a building architect will create wiring diagrams, floor plans, and elevations to describe
different facets of a building to its different stakeholders (electricians, owners, planning officials), so an
enterprise architect must create different views of the business, information system, and technology architecture for
the stakeholders who have concerns related to these aspects.
TOGAF specifically identifies this issue throughout the ADM through the following concepts (as defined in Architectural Artifacts):
-
Stakeholders
-
Concerns
-
Views
-
Viewpoints
Steps in the Stakeholder Management Process
The following sections detail recommended Stakeholder Management activity.
Identify Stakeholders
Identify the key stakeholders of the enterprise architecture.
The first task is to brainstorm who the main enterprise architecture stakeholders are. As part of this, think of all
the people who are affected by it, who have influence or power over it, or have an interest in its successful or
unsuccessful conclusion.
It might include senior executives, project organization roles, client organization roles, system developers, alliance
partners, suppliers, IT operations, customers, etc.
When identifying stakeholders there is a danger of concentrating too heavily on the formal structure of an organization
as the basis for identification. Informal stakeholder groups may be just as powerful and influential as the formal
ones.
Most individuals will belong to more than one stakeholder group, and these groups tend to arise as a result of specific
events.
Look at who is impacted by the enterprise architecture project:
-
Who gains and who loses from this change?
-
Who controls change management of processes?
-
Who designs new systems?
-
Who will make the decisions?
-
Who procures IT systems and who decides what to buy?
-
Who controls resources?
-
Who has specialist skills the project needs?
-
Who has influence?
In particular, influencers need to be identified. These will be well respected and moving up, participate in important
meetings and committees (look at meeting minutes), know what's going on in the company, be valued by their peers and
superiors, and not necessarily be in any formal position of power.
Although stakeholders may be both organizations and people, ultimately the enterprise architecture team will need to
communicate with people. It is the correct individual stakeholders within a stakeholder organization that need to be
formally identified.
It is possible to distinguish five broad categories of stakeholder, as shown below:
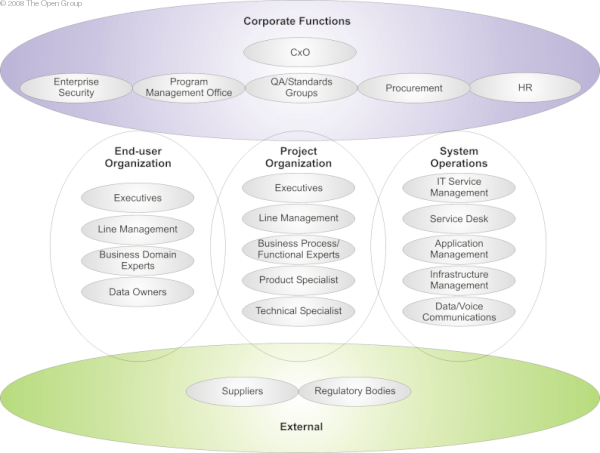 Figure: Categories of Stakeholder
Figure: Categories of Stakeholder
Consider both the Visible team - those obviously associated with the project/change - and the Invisible team - those
who must make a real contribution to the project/change for it to be successful but who are not obviously associated
with it (e.g., providers of support services).
Classify Stakeholder Positions
Develop a good understanding of the most important stakeholders and record this analysis for reference and refresh
during the project. An example stakeholder analysis is shown below:
|
|
Ability to
|
Current
|
Required
|
|
|
|
|
Stakeholder
|
|
Disrupt
|
Under-
|
Under-
|
Current
|
Required
|
Required
|
|
Group
|
Stakeholder
|
Change
|
standing
|
standing
|
Commitment
|
Commitment
|
Support
|
|
CIO
|
John Smith
|
H
|
M
|
H
|
L
|
M
|
H
|
|
CFO
|
Jeff Brown
|
M
|
M
|
M
|
L
|
M
|
M
|
Table: Example Stakeholder Analysis
It is also important to assess the readiness of each stakeholder to behave in a supportive manner (i.e., demonstrate
commitment to the enterprise architecture initiative).
This can be done by asking a series of questions:
-
Is that person ready to change direction and begin moving towards the Target Architecture? If so, how ready?
-
Is that person capable of being a credible advocate or agent of the proposed enterprise architecture initiative? If
so, how capable?
-
How involved is the individual in the enterprise architecture initiative? Are they simply an interested observer,
or do they need to be involved in the details?
-
Has that person made a contractual commitment to the development of the enterprise architecture, and its role in
the governance of the development of the organization?
Then, for each person whose commitment is critical to ensure success, make a judgment as to their current level of
commitment and the desired future level of commitment.
Determine Stakeholder Management Approach
The previous steps identified a long list of people and organizations that are affected by the enterprise architecture
project.
Some of these may have the power either to block or advance. Some may be interested in what the enterprise architecture
initiative is doing; others may not care. This step enables the team to easily see which stakeholders are expected to
be blockers or critics, and which stakeholders are likely to be advocates and supporters of the initiative.
Work out stakeholder power, influence, and interest, so as to focus the enterprise architecture engagement on the key
individuals. These can be mapped onto a power/interest matrix, which also indicates the strategy to adopt for engaging
with them. Stakeholder Power Grid shows an example power grid matrix.
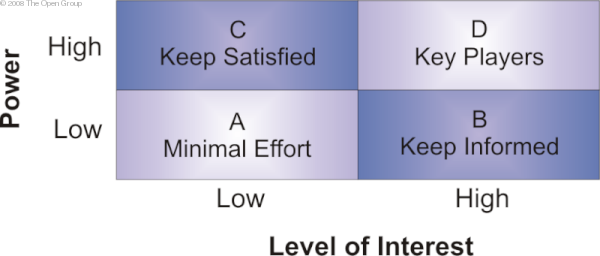 Figure: Stakeholder Power Grid
Figure: Stakeholder Power Grid
Tailor Engagement Deliverables
Identify viewpoints, matrices, and views that the architecture engagement needs to produce and validate with each
stakeholder group to deliver an effective architecture model.
It is important to pay particular attention to stakeholder interests by defining specific viewpoints, matrices, and
views of the enterprise architecture model. This enables the architecture to be communicated to, and understood by, all
the stakeholders, and enables them to verify that the enterprise architecture initiative will address their concerns.
Template Stakeholder Map
The following table provides an example stakeholder map for a TOGAF architecture project.
|
|
|
Relevant
|
|
Stakeholder
|
Involvement
|
Class
|
Viewpoints
|
|
CxO
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., CEO, CFO, CIO, COO
|
This stakeholder group is interested in the high-level drivers, goals, and objectives of the
organization, and how these are translated into an effective process and IT architecture to advance
the business.
|
KEEP SATISFIED
|
Business Footprint
Goal/Objective/ Service Model
Organization Chart
|
|
Program Management Office
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Project Portfolio Managers
|
This stakeholder group is interested in prioritizing, funding, and aligning change activity. An
understanding of project content and technical dependencies between projects adds a further
dimension of richness to portfolio management decision-making.
|
KEEP SATISFIED
|
Roadmaps
Business Footprint
Application Communication
Functional Decomposition
|
|
Procurement
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Acquirers
|
Major concerns for these stakeholders are understanding what building blocks of the architecture
can be bought, and what constraints (or rules) exist that are relevant to the purchase. The
acquirer will shop with multiple vendors looking for the best cost solution while adhering to the
constraints (or rules) applied by the architecture, such as standards. The key concern is to make
purchasing decisions that fit the architecture, and thereby to reduce the risk of added costs
arising from non-compliant components.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Cost View
Standards View
|
|
Human Resources (HR)
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., HR Managers, Training & Development Managers
|
Key features of the enterprise architecture are the roles and Actors that support the functions,
applications, and technology of the organization. HR are important stakeholders in ensuring that
the correct roles and actors are represented.
|
KEEP INFORMED
|
Organization Chart
Organization/Actor/ Location
|
|
Enterprise Security
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Corporate Risk Management, Security Officers, IT Security Managers
|
Major concerns for this group are understanding how to ensure that the information, data, and
systems of the organization are available to only those that have permission, and how to protect
the information, data, and systems from unauthorized tampering.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Data Security View
Networked Computing Hardware View
Communications View
|
|
QA/Standards Group
(Corporate Functions);
e.g., Data Owners, Process Owners, Technical Standards Bodies
|
Major concerns for this group are ensuring the consistent governance of the organization's
business, data, application, and technology assets.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Standards
Guidelines
Specifications
Standards View
Application Portfolio
Technology Portfolio
Technology Standards
|
|
Executive
(End User Organization);
e.g., Business Unit Directors, Business Unit CxOs, Business Unit Head of IT/Architecture
|
This stakeholder group is interested in the high-level drivers, goals, and objectives of the
organization, and how these are translated into an effective process and IT architecture to advance
the business.
|
KEEP SATISFIED
|
Business Footprint
Goal/Objective/ Service Model
Organization Chart
|
|
Line Management
(End User Organization);
e.g., Senior Business Managers, Operations Regional Managers, IT Managers
|
This stakeholder is interested in the top-level functions and processes of the organization, and
how the key applications of the IT estate support these processes.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Organization/Actor/ Location
Goal/Objective/ Service Model
Cost View
Application & User Location View
|
|
Business Domain Experts
(End User Organization);
e.g., Business Process Experts, Business/Process Analyst, Process Architect, Process Designer,
Functional Managers, Business Analyst
|
This stakeholder is interested in the functional aspects of processes and systems. This can cover
the human actors involved in the system, the user processes involved in the system, the functions
required to support the processes, and the information required to flow in support of the
processes.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Process Flow
Use-case
Service/Information Events
Functional Decomposition
Application - Application Communication View
Data Entity/Business Function Matrix
|
|
IT Service Management
(Systems Operations);
e.g., Service Delivery Manager
|
Major concerns for this group are ensuring that IT services provided to the organization meet the
service levels required by that organization to succeed in business.
|
KEEP INFORMED
|
Standards View
Enterprise Manageability View
|
|
IT Operations - Applications
(System Operations);
e.g., Application Architecture, System & Software Engineers
|
Major concerns for these stakeholders are: Development Approach, Software Modularity and Re-use,
Portability Migration, and Interoperability.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Process - System Realization View
Application - Data View
Application Migration Cost View
Software Engineering View
Platform Decomposition View
Networked Computing - Hardware View
Software Distribution View
Data Entities to Application Systems View
|
|
IT Operations - Infrastructure
(System Operations);
e.g., Infrastructure Architect, Wintel support, Mid-range support, Operational DBA, Service Desk
|
Infrastructure stakeholders are typically concerned with location, modifiability, re-usability, and
availability of all components of the system. In general these stakeholders are concerned with
ensuring that the appropriate components are developed and deployed within the system in an optimal
manner.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Platform Decomposition View
Standards View
Enterprise Manageability View
Networked Computing - Hardware View
Processing View
Environments & Locations View
|
|
IT Operations - Data/Voice Communications
(System Operations);
e.g., Network Management
|
Communications engineers are typically concerned with location, modifiability, re-usability, and
availability of communications and networking services. In general these stakeholders are concerned
with ensuring that the appropriate communications and networking services are developed and
deployed within the system in an optimal manner.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Communications View
|
|
Executive
(Project Organization);
e.g., Sponsor, Program Manager
|
This stakeholder group is interested in on-time, on-budget delivery of a change initiative that
will realize expected benefits for the organization.
|
KEEP INFORMED
|
Architecture Requirements
Architecture Principles
Architecture Vision
Functional Decomposition
Application & User Location View
|
|
Line Management
(Project Organization);
e.g., Project Manager
|
This stakeholder group is responsible for operationally achieving on-time, on-budget delivery of a
change initiative with an agreed scope.
|
KEEP INFORMED
|
Application - Application Communication View
Functional Decomposition
Environments & Locations View
|
|
Business Process/Functional Expert
(Project Organization);
e.g., Financials FICO Functional Consultant, HR Functional Consultant
|
This stakeholder group will elaborate the functional requirements of a change initiative based on
experience and interaction with business domain experts in the end-user organization.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Process Flow
Use-case
Service/Information Events
Functional Decomposition
Application - Application Communication View
|
|
Product Specialist
(Project Organization);
e.g., Portal Product Specialist
|
This stakeholder group is responsible for specifying technology product designs in order to meet
project requirements and comply with the Architecture Vision of the solution.
In a packages and packaged services environment, product expertise can be used to identify product
capabilities that can be readily leveraged and can provide guidance on strategies for product
customization.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Software Engineering View
Application - Data View
|
|
Technical Specialist
(Project Organization);
e.g., Application Architect
|
This stakeholder group is responsible for specifying technology product designs in order to meet
project requirements and comply with the Architecture Vision of the solution.
|
KEY PLAYERS
|
Software Engineering View
Platform Decomposition View
Process System
Realization View
Application - Data View
Application Migration Cost View
|
|
Regulatory Bodies
(Outside Services);
e.g., Financial Regulator, Industry Regulator
|
The main concerns of this group are that they can receive the information they need in order to
regulate the client organization, and that their information requirements are being understood and
properly satisfied. They are specifically interested in reporting processes, and the data and
applications used to provide regulatory return information.
|
KEEP SATISFIED
|
Business Footprint
Application - Application Communication View
|
|
Suppliers
(Outside Services);
e.g., Alliance Partners, Key Suppliers
|
The main concerns of this group are that the information exchange requirements that they have are
met in order that agreed service contracts with the client organizations can be fulfilled.
|
KEEP SATISFIED
|
Business Footprint
Service-Information View
Application - Application Communication View
|
|

